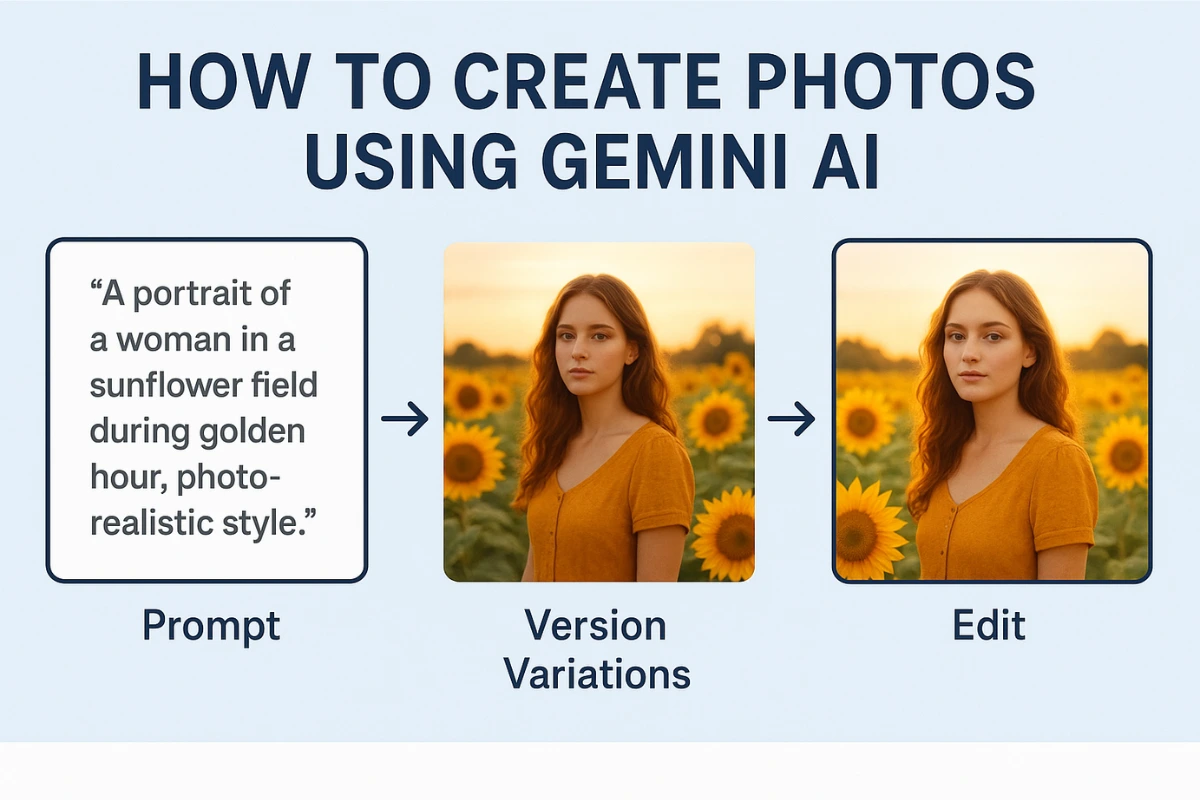
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools have transformed how we create visuals. Google’s Gemini (often called Gemini AI) is one such tool that allows users to generate images and photos from textual descriptions. Here’s a guide to help you produce great photos using Gemini AI—step by step.
What is Gemini AI?
Gemini AI is an AI-based image generation and editing platform by Google. It allows users to input text prompts, and from those, generate high-quality images with style, composition, and other artistic or photographic traits. It also supports editing of existing images, applying styles, making local changes, etc.
Step-by-Step: Creating a Photo with Gemini AI
Here are the steps to go from idea → prompt → final image:
| Step | What to do | Tips for better results |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define your concept | Decide what you want: the subject, environment, mood, style. e.g. “a portrait of a woman in a sunflower field during golden hour, photorealistic style.” | Being specific helps. The more details—lighting, mood, color palette, composition—the better. |
| 2. Write a good prompt | In your prompt include subject (who/what), setting (where), action or activity (what is happening), style or aesthetic, lighting, camera angle if relevant. | Use descriptive adjectives (e.g., dreamy, cinematic, sharp, warm light), mention style references if you like (e.g. “in the style of film photography”, “oil painting”, “digital art”). |
| 3. Choose dimensions / aspect ratio | Gemini may allow specifying the image size or aspect ratio (portrait, widescreen, square) to suit where you want to use the image (Instagram post, website header, print, etc.). | Pick the right ratio ahead of time so you don’t need extensive cropping later. |
| 4. Generate initial image(s) | Submit the prompt. Gemini will generate one or more variants. | Sometimes experimenting with more than one variant helps—you can pick the best or combine ideas. |
| 5. Refine / edit | Use Gemini’s editing options if available: change colors, remove objects, adjust lighting, change the background, fine-tune style. | Be precise when asking for edits: e.g. “make the sky more orange”, “remove the object on the left”, “add lens flare”. |
| 6. Review and iterate | View the image, check for things that don’t match your vision. Rerun prompt with tweaks or edit directly. | It might take several rounds to get it close to what you want. Save earlier versions if you like aspects of each. |
| 7. Export / use | Once satisfied, export the image at suitable resolution. Save or share. | Keep a high-res copy; if using commercially, check licensing or terms of use. |
Tips for Getting the Best Output
-
Use reference styles: Mention known artists, photographers, styles (e.g. “Rembrandt style lighting”, “modern architecture photography”) so the AI has direction.
-
Focus on lighting: Light direction, time of day, shadows, color temperature—all very crucial to mood.
-
Composition matters: Frame elements properly—rule of thirds, leading lines, negative space etc.—these help produce more professional-looking photos.
-
Simplify when needed: If the prompt is too complicated (too many conflicting ideas), output may be messy. Sometimes simpler prompts with fewer but more clear instructions work better.
-
Iterate & experiment: Don’t expect perfection first try. Try variations, tweak small details.
-
Mind resolution & use case: If you need for print, choose higher resolution; for social media maybe less. Also consider usage rights.
Also read: GPT-5 Unveiled: OpenAI’s Most Powerful AI Emerges
Possible Challenges & How to Overcome Them
-
Inconsistent details: Sometimes facial features or items may differ across variants. Solution: emphasize consistency in prompt (“same character”, “same facial structure”, etc.).
-
Unwanted artifacts / distortions: AI may misinterpret details (hands, eyes, text, small objects). Solution: use the editing tools; request corrections.
-
Style mismatch: You might ask for one style but get something in between. Solution: specify more clearly, give style references, or do part of the prompt as “in the style of X”.
-
Resolution limits: If resolution isn’t high, image may be blurry if enlarged. Solution: generate at highest possible resolution; upscaling tools might help after.
Use-Cases
Some examples of where Gemini-AI generated photos are useful:
-
Social media posts and marketing content
-
Blog/website featured images
-
Digital art & concept visuals
-
Illustrations for presentations, ebooks
-
Mockups for design, fashion, interior, etc.
Ethics & Best Practices
-
Always check the terms of use of Gemini—usage, licensing, commercial permissions.
-
Be mindful of producing images that might infringe copyright (e.g. copying identifiable brand logos) or likeness rights (if using real people).
-
Use AI-generated photos responsibly; disclose when images are AI-created in contexts where that matters (e.g. journalism, advertising).
-
Respect privacy and avoid generating harmful or misleading content.
Gemini AI gives powerful tools to transform your imagination into visual reality. With a well-thought prompt, attention to style, lighting and composition,—and some iteration—you can create striking, professional images. Whether you’re a marketer, designer, creator, or hobbyist, mastering prompt craft and refinement will help you make the most out of Gemini AI.